Resistance
The resistance in a circuit is the opposition to the flow of current.
The unit of resistance is Ohm [Ω].
- Some components in a circuit such as a bulb or a heater have resistance.
- A device which provides some resistance in the circuit is called a resistor
- A resisitor which can vary resistance is called the rheostat.
Formula
Given that
R: Resistance [Ω]
V: Potential difference [V]
I: Current [A]
This relationship is called Ohm’s law.
Example 1
A current of 2A flows through a conductor. The conductor has the p.d. of 12V. Find the resistance of the conductor.
Solution
Given that
I = 2A
V = 12V
R = ?
Answer:
Example 2
Find the p.d. across a 1.5Ω resistor when a current of 4A flows through it.
Solution
Given that
R = 1.5Ω
I = 4A
V = ?
Answer:
Example 3
Find the current flowing through a 5Ω resistor that has 20V across it.
Solution
Given that
R = 5Ω
V = 20V
I = ?
Answer:
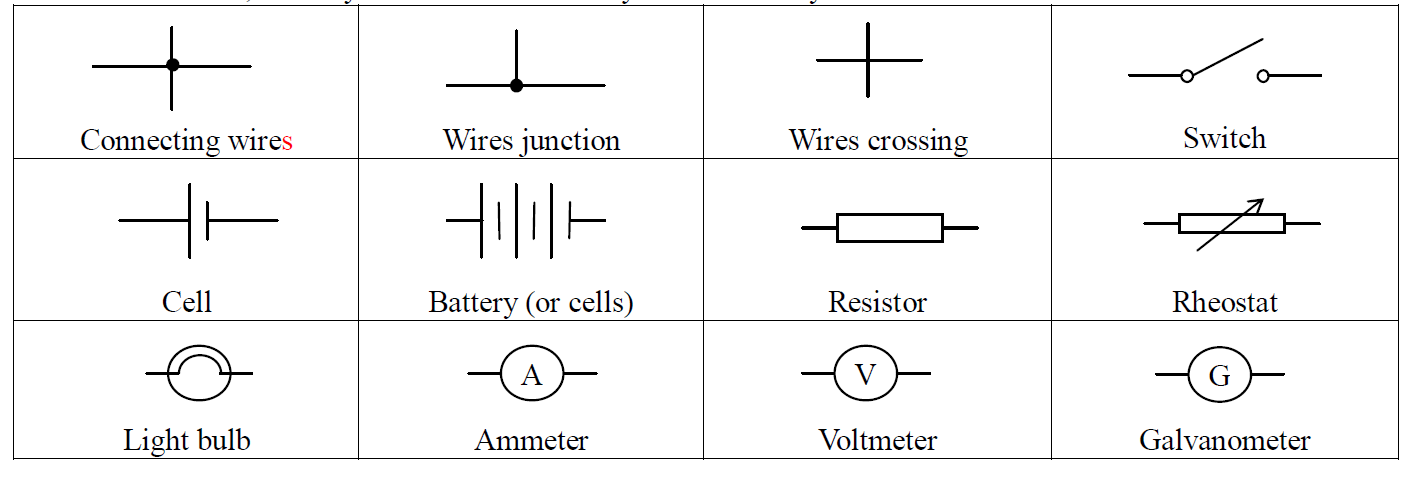
Symbol of electrical component
When we draw a circuit, some symbols are used. The symbols comonly used are shown below.
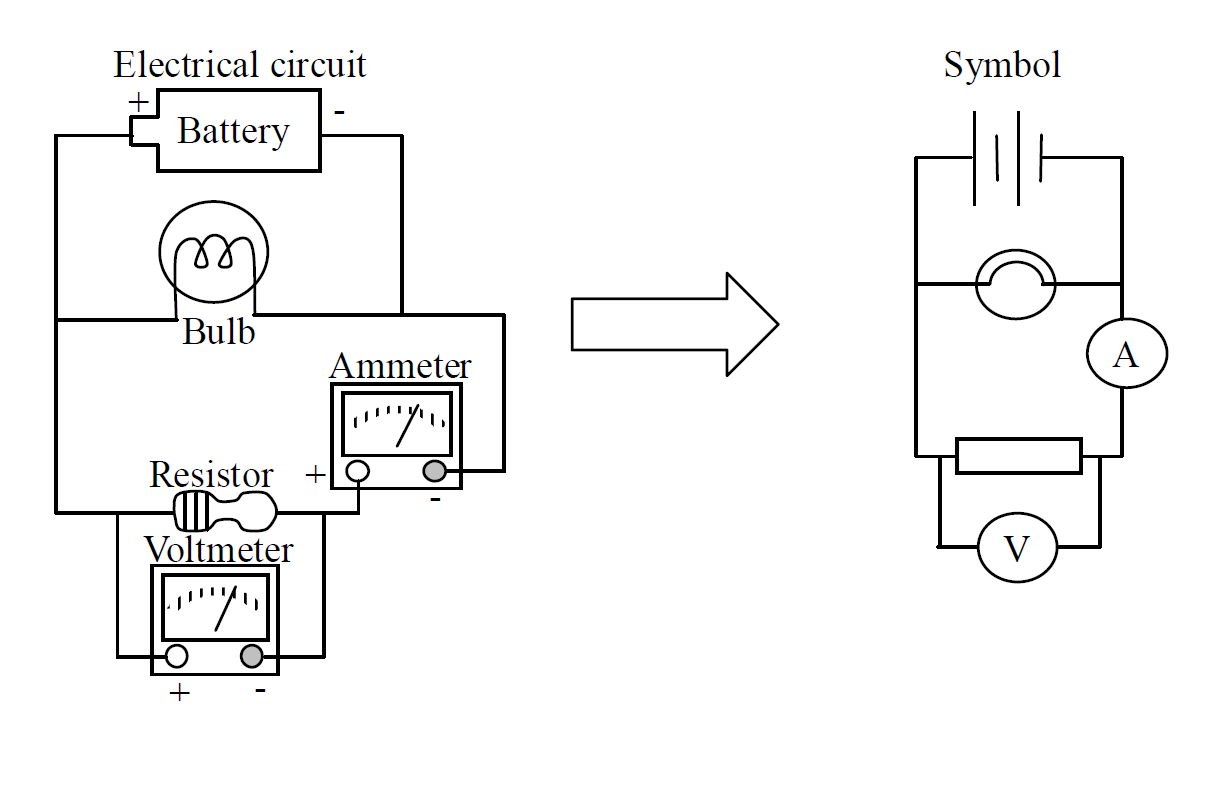
Example
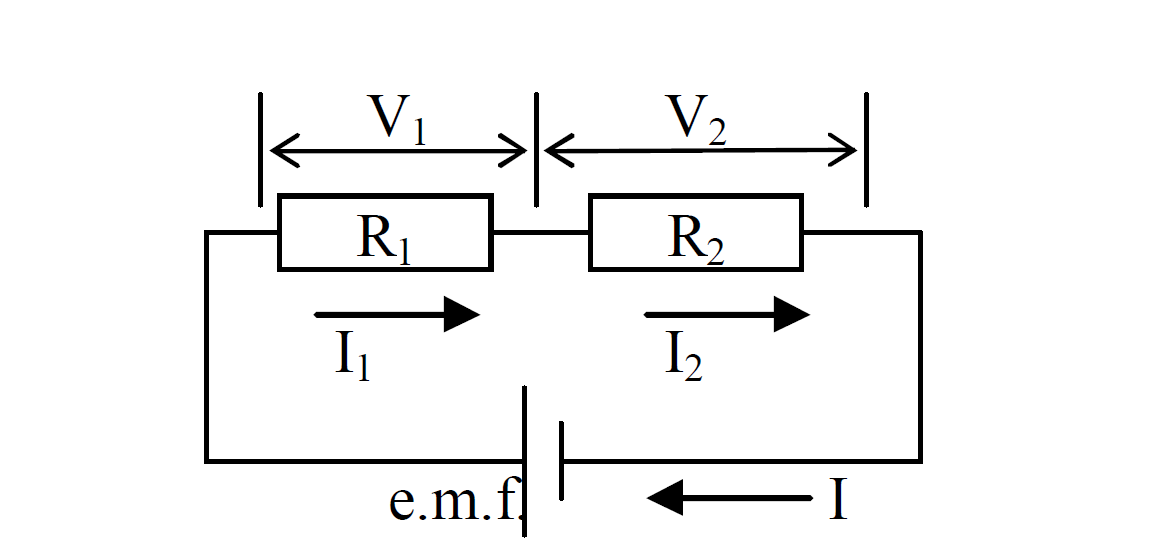
Series circuit
- The current is the same at all points in the series circuit.
- The sum of the p.d. V across the resistors (the total resistance) is the same as the e.m.f.
= The total resistance, R, of the components connected in series circuit is equal to the sum of the separate resistances.
Example
Given the circuit below, Find
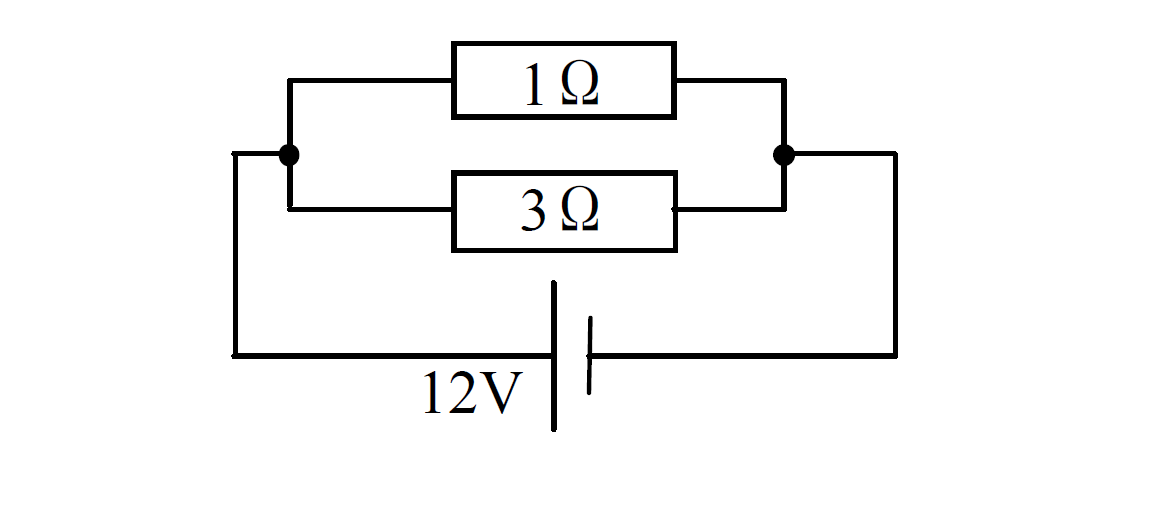
(a) the total resistance
(b) the p.d. of 1Ωresistor.
(c) the p.d. of 3Ω resistor.
(d) the current through 1Ω resistor.
(e) the current through 3Ω resistor.
(f) the current through the cell.
Solutions
(a)
Given that
R1 = 1Ω
R2 = 3Ω
R = ?
Answer:
(b)
e.m.f. = 12V
Answer:
(c)
e.m.f. = 12V
Answer:
(d)
Given that
V1 = 12V
R1 = 1Ω
I1 = ?
Answer:
(e)
Given that
V2 = 12V
R2 = 3Ω
I2 = ?
Answer:
(f)
Given that
I = ?
I1 = 12A
I2 = 4A
Answer: